Energy from Waste
Today, since the importance of recycling is increasing gradually, researches are carried out on various systems by scientists to recycle waste.
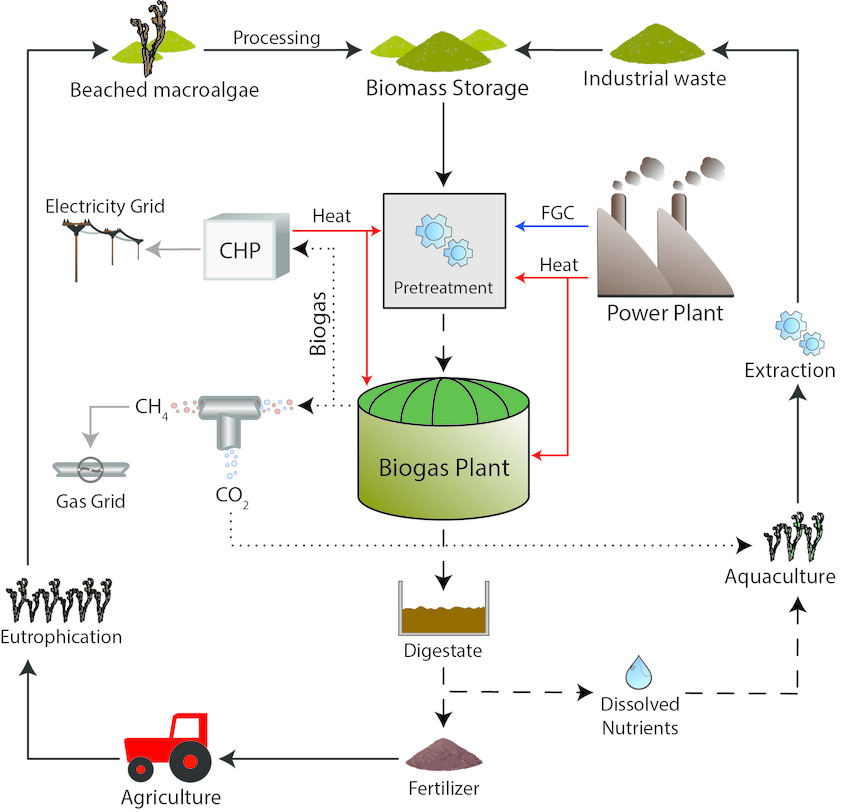
Biogas is a kind of usable gas produced from organic wastes. It is obtained by the conversion of organic materials into carbon dioxide and methane gas by microbiological creatures, in an oxygen-free environment. Materials used in biogas production are grouped as animal fertilizers, organic wastes, and industrial wastes.
Points to Consider for Biogas Production from Organic Waste:
- There should never be oxygen in the production tank.
- Wastes which belongs to animals given antibiotics should not be taken into the production tank.
- Detergent-containing organic wastes should not be taken into the production tank.
- For new bacteria to form and grow, the nitrogen amount in the environment should be sufficient.
- In the production tank, the pH value should be between 7.0 and 7.6.
- For methane bacteria, the concentration of organic acid in the substrate (S) in terms of acetic acid should be in the range of 500–1500 mg/liter.
The calorific value provided by 1m3 of biogas is 4700-5700 kcal/m3. This value is equivalent to approximately 0.62 liters of gas oil, 1.46 kg of charcoal, 3.47 kg of wood, 0.43 kg of butane gas, 12.3 kg of dung, 4.70 kWh of electrical energy.
Biogas Plants
Biogas facilities are divided into 4 groups according to their capacities;
- Family type: 6-12 m3 capacity,
- Farm type: 50-100-150 m3 capacity,
- Village type: 100-200 m3 capacity,
- Industrial scale facilities: 1000-10.000 m3 capacity.
Biogas systems are highly sensitive to instant temperature changes. In the case of a 1-2° C decline or rise in the reactor temperature in less than 2 hours, biogas production is adversely affected. If the temperature fluctuation affects the methane-producing arcs in the system, it may take weeks to regain the same efficiency level in methane production.
According to the operating temperature, biogas reactors are classified as follows:
- psychrophilic (15-20°C),
- mesophilic (30-38°C)
- thermophilic (50-60°C).
Also, the content of biomass has significance to the production of biogas from organic wastes. Some substances contained in biomass may cause inhibition during biogas production. These substances can be listed as follows:
- Long chain or volatile fatty acids,
- Ammonia (NH3),
- Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S),
- Heavy metals (Zn, Cd, Cu, Ni, Cr, Pb, Co etc.),
- Alkaline metals (Na, K, Ca, Mg),
- Human structure is an example of difficult chemicals to degrade (chlorinated hydrocarbons).